Key highlights
- Existing EV charging networks aren’t currently meeting consumer demand, and compatibility issues remain a challenge.
- Road fatalities spiked during the COVID-19 pandemic, and government entities are trying new approaches to promote safe driving.
- Electric and hybrid trucks are hitting the mainstream, challenging previously-held perceptions of electric vehicle models.
- Despite the climate-related benefits of electric vehicles, financial and regulatory challenges prevent widespread adoption.
- Consumer distrust of self-driving vehicles is increasing, likely due to high-profile EV crashes over the past two years.
|
Governments and corporations are looking for ways to expand EV charging networks.
The demand for reliable, widespread charging options is increasing with the release of new electric vehicle models. Right now, Tesla’s proprietary Supercharger network is widely considered to be the most powerful and reliable option. However, most other EV models aren’t currently compatible with Superchargers.
As a result, many EV manufacturers plan on switching to NACS ports in the coming years, which will be compatible with Tesla’s chargers. Brands like Ford, GM, BMW, Hyundai, and Kia have all recently announced that their 2025 EV models will be Supercharger-compatible.

However, this hasn’t stopped manufacturers from launching their own charging networks as well. GM recently partnered with Pilot Travel Centers to open 17 fast-charging EV stations throughout the United States. Internationally, British sports car manufacturer Lotus is planning their own EV fast-charging network. Lotus already has chargers operating in China and plans to expand throughout Europe and the Middle East.
GM will also be one of seven automakers partnering to launch a new charging network that will be compatible with both CCS and NACS EV models. This network will operate throughout the United States and could rival the Supercharger network. Other partners include BMW, Honda, Hyundai, Kia, Mercedes-Benz, and Stellantis.
As charging networks remain a challenge, startups continue to look for alternative solutions. Notably, the first inductive-charging road for electric vehicles has debuted in Detroit. This road is a quarter-mile long and uses specialized induction coils to charge compatible EVs as they drive. The project was a partnership with startup Electreon and the state of Michigan. Electron plans to explore more efficient charging applications, which would potentially involve inductive charging at traffic lights and bus stops.
With spikes in car crashes and thefts, regulatory bodies are looking for ways to make roads safer.
Road fatalities increased during the COVID-19 pandemic, with a year-over-year increase of 18.4% from 2020 to 2021. Although this spike in crash-related deaths has since slowed down, automotive regulatory bodies in the United States continue to look for ways to mitigate future crashes.
The National Transportation Safety Board recently asked 17 leading car manufacturers to add speed limiting technology to new vehicles. At minimum, these vehicles would include speed warning systems, but some would take more intensive preventative measures. This comes after a July study from AAA that indicated that raising speed limits is unlikely to shorten commutes, but could make those commutes far more dangerous for everyone on the road.
Additionally, the NTSB has expressed interest in removing stunt driving from car commercials. They plan to work with the Insurance Institute of Highway Safety to research the relationship between stunt driving in marketing and reckless driving behaviors. A correlation has yet to be established between these two behaviors.
Wildlife-related crashes have also been cause for concern, as more than 1 million of these crashes happen annually. The US Department of Transportation recently awarded a total of $110 million to develop safe wildlife crossings. These projects include overpass development, wildlife fencing, and even GPS tracking to keep wildlife safely off the road.
In the United Kingdom, another safety threat has emerged — keyless car thefts. With these thefts, Research from insurance company LV General indicates that there was a 59% year-over-year increase in overall car thefts in 2022, with 2023 rates shaping up to be even higher. The UK government has proposed a law to outlaw the electronic relay devices that are used in these incidents, but has yet to crack down on sales.

Electric and hybrid trucks are some of the hottest cars of 2024, led by the release of the much-hyped Tesla Cybertruck.
When you think of a stereotypical electric vehicle, you might think of a vehicle that’s sleek, compact, or unobtrusive. This could change in 2024 with electric and hybrid truck models trending. Many car manufacturers have developed vehicles that combine the traditionally rugged features of a truck with a more eco-friendly electric transmission.
This trend has taken off with Tesla’s Cybertruck, which was released at the end of November after years of development. The Cybertruck is noted for its futuristic design with an angular stainless steel frame and “shatter-resistant” acoustic glass. However, there have been some concerns about the vehicle’s battery life. The Cybertruck will go an estimated 340 miles on a full charge with a battery capacity of 122.4 kWh, which is lower than many of its competitors.
Speaking of competitors, the Cybertruck isn’t the only electric truck to take the market by storm. In October 2023, the Ford F-150 Lightning hit a new US sales record, with sales up 52% year-over-year.
Get the key highlights of the automotive industry directly to your mailbox.
Changing regulations and price fluctuations present barriers to widespread EV adoption.
A societal push towards electric vehicles has been growing for the last decade, with a focus on reducing the auto industry’s negative impact on the global climate. However, financial and cultural barriers continue to prevent widespread EV adoption.
One of the biggest barriers to EV adoption for many consumers is cost, particularly in today’s challenging economy. While EVs make up more than one-third of the luxury vehicle market in the United States, the average EV transaction cost in the third quarter of 2023 was $50,283. This puts an electric vehicle purchase out of reach for the average consumer.
Changes to EV regulations and policies in the United States could further limit the adoption of electric vehicles. The US government currently offers a federal tax credit of $7,500 for those who purchase an electric vehicle. However, the US Departments of Treasury and Energy recently announced plans to limit eligibility for this tax credit for EVs that contain battery materials made in China.
These plans are designed to limit the US’s dependency on China and other foreign entities for EV development. However, these new tax credit restrictions could make EVs even less affordable for consumers. Europe and the United Kingdom have also considered tariffs on Chinese-produced car batteries. However, the European Commission recently announced a three-year postponement of these tariffs.
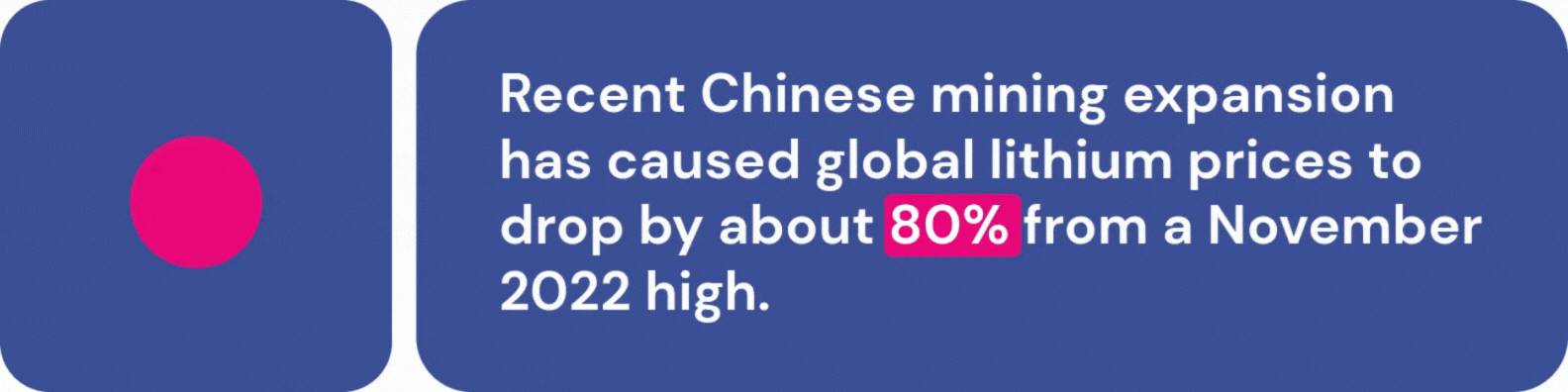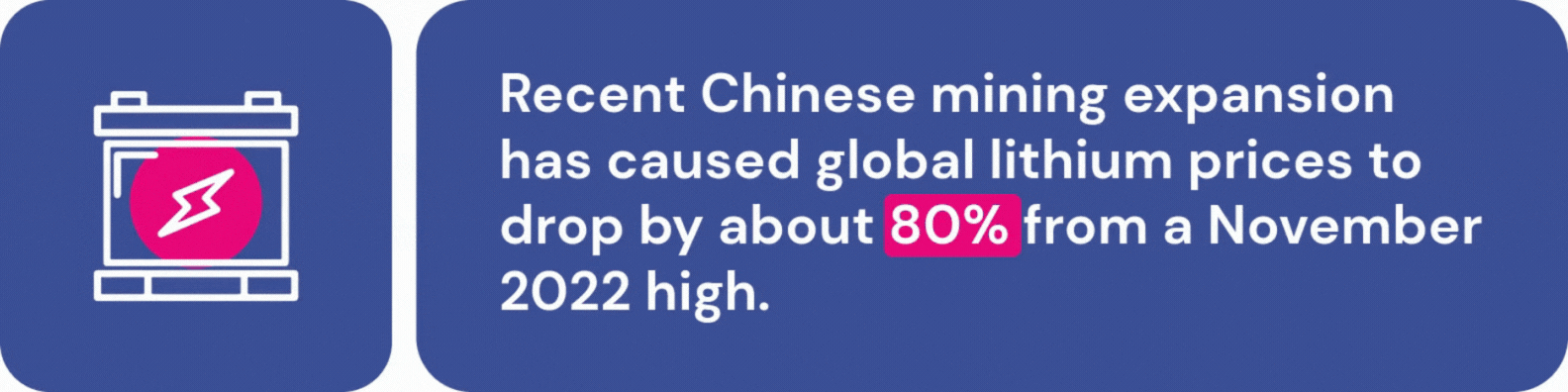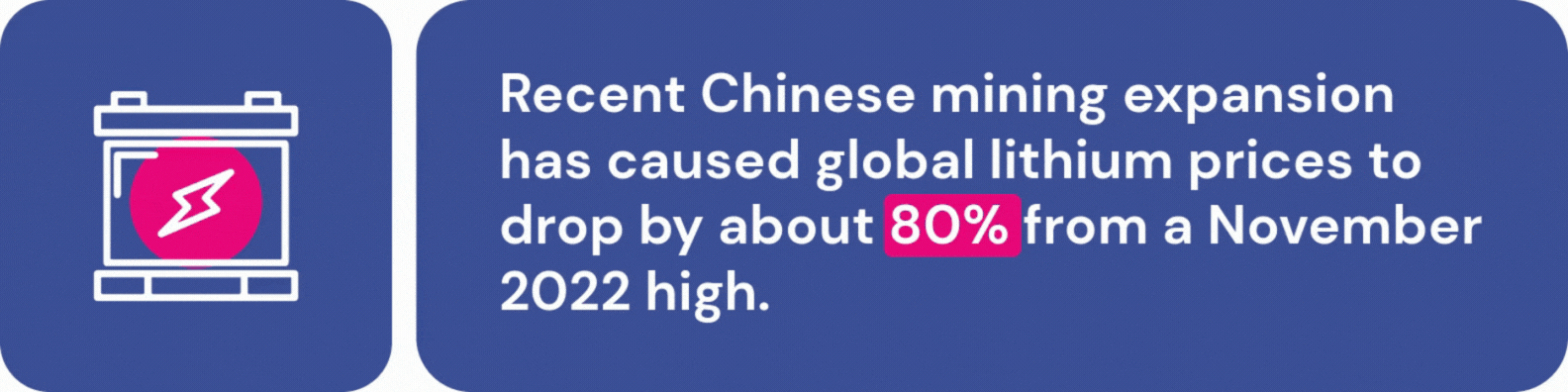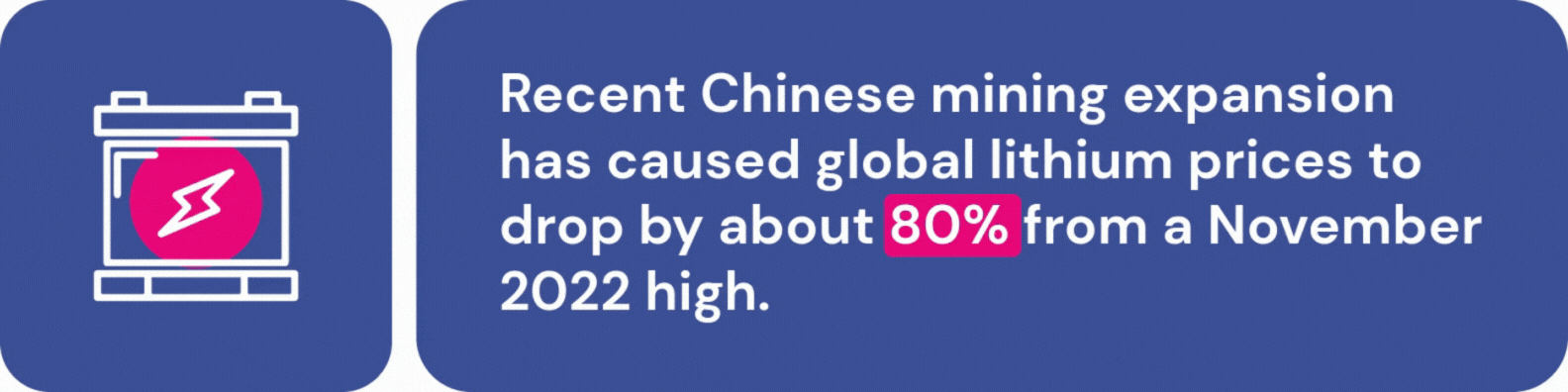
EV accessibility is further complicated by supply chain challenges. Fears of a lithium shortage abound, although recent Chinese mining expansion has caused global lithium prices to drop by about 80% from a November 2022 high. While this should keep battery production stable in the short term, many experts worry about lithium availability as demand for EVs continues to rise. Additionally, the Chinese government recently announced that they will require government approval for graphite exports, which are a crucial part of EV manufacturing.
Consumers are skeptical about self-driving and driver-assisted vehicles.
For years, self-driving cars appeared to be on the precipice of mainstream adoption. However, customers remain skeptical about self-driving and driver-assisted vehicles — and it’s having real repercussions in the auto market.
A report from J.D. Power earlier this year found that consumers are slowly losing trust in self-driving vehicles. Electric vehicles scored a 37 out of 100 on the company’s Mobility Conference Index, a two-point drop from 2022. Researchers cited a lack of general knowledge about autonomous vehicles as well as negative media coverage for these perceptions.

Some of this negative media coverage came from a fleet of self-driving Chevy Bolt EVs in San Francisco. These vehicles were prototypes for Cruise, a subsidiary of General Motors focused on self-driving cars.
Cruise’s vehicles have been involved in multiple crashes throughout the city, resulting in recalls and potential fines. At the end of October, California revoked Cruise’s self-driving permits. The organization had been developing the Cruise Origin driverless pod, but production is now delayed indefinitely.
Growing distrust in autonomous vehicles has also affected Luminar, a company leading the charge in AV lidar sensors. Luminar’s sensors are designed to support autonomous driving on highways and prevent crashes. However, the company’s stock dropped drastically in late November, likely due to consumer distrust in autonomous vehicles.